a) neutral (0,0): neither species affects the DIRECTLY, eg. eagles and grass
 |
| Eagle landing |
b) commensalim (+,0): 1 benefits without affecting the other significantly, eg. birds on trees, remoras on sharks, sparrows on the edge of a stork's nest, clownfish and sea anemone
 |
| Remora and shark |
c) mutualism/symbiosis (+,+): each receives a benefit from the other, eg. liches, mycorrhizae, legumes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria, ruminants and cellulose-digesting bacteria, termites and cellulose-digesting protozoa, gardener ants and fungus, hermit crabs and sea anemones, ants and aphids
 |
| Micorrhizae |
 |
| Symbiosis of sea anemone and hermit crab |
d) parasitism (+,-): 1 benefits, while the other is harmed, eg. viruses and host, fleas and dogs (ectoparasite), tapeworms and dogs (endoparasite), mistletoe and trees
 |
| Mistletoe |
e) predation (+,-): predator benefits, prey is harmed
 |
| Predation |
f) antibiosis/amensalism (0,-): 1 harms the other but has no benefit from it eg. Penicillium fungus and bacteria, algae bloom and fish
 |
| Harposporium showing antibiosis |
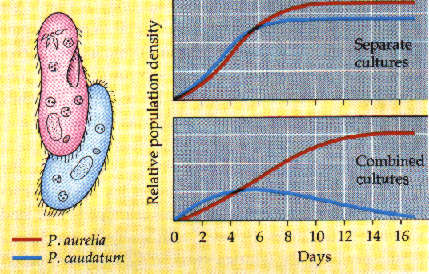
g) competition (-,-): both use the same resources, can be intraspecific or interspecific
 |
| Intraspecific competition |
 |
| Interspecific competition |
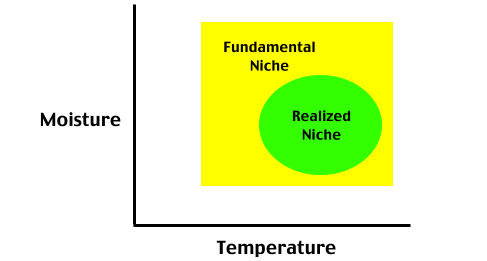
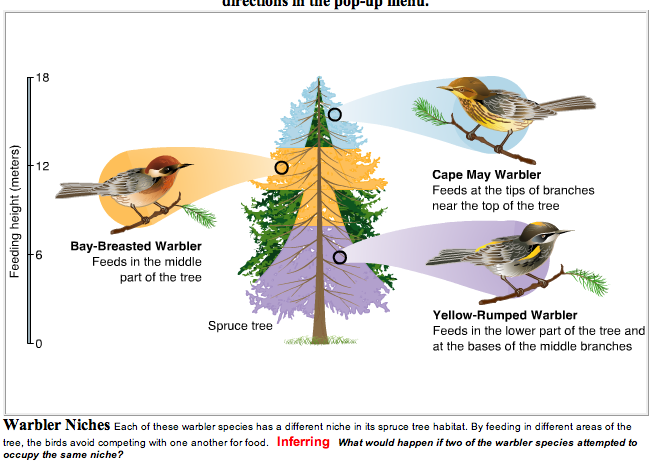
The competitive exclusion theory (Gauze's theory) states that no two species can occupy the same niche in the same environment for a long time. If species with the same
fundamental niches live in the same area, then their
realized niches must be different from each other.










No comments:
Post a Comment